OpenAPI Schemas¶
porter provides support for automatically validating and documenting payload schemas. Validation and documentation are built on a shared interface, guaranteeing that the documentation and models are synchronized. For additional information, we recommend taking a look at this script which contains several working examples.
Note
Currently porter validates data against OpenAPI schemas by leveraging fastjsonschema. This implies that porter currently only supports the intersection of OpenAPI and JSONSchema which is described here.
At the moment this is simply an implementation detail. Any changes in the future would provide more broad support for the OpenAPI spec.
Schema Definition¶
porter provides a Python interface to the OpenAPI Specification. Schema definition is facilitated by porter.schemas. Valid data types include:
from porter.schemas import Boolean, Integer, Number, String, Array, Object
For each type, the first argument is an optional (but recommended) description.
Objects take a properties argument of type dict specifying the names and types of each nested element. All types take an optional additional_params argument, also of type dict, giving access to all other keys in the OpenAPI specification.
For example, the input expected by a porter.services.PredictionService serving rating predictions might look like so:
feature_schema = Object(
'Inputs to the ratings model',
properties=dict(
user_id=Integer('The user ID.'),
title_id=Integer('The title ID.'),
is_tv=Boolean('Whether the content is a TV show.'),
genre=String('The genre.',
additional_params={'enum': ['comedy', 'action', 'drama']}),
average_rating=Number('The title\'s average rating.',
additional_params={'minimum': 0, 'maximum': 10}),
),
reference_name='RatingsModelFeatures'
)
This schema is equivalent to the following yaml markup:
- RatingsModelFeatures:
type: object
description: Inputs to the ratings model
properties:
user_id:
type: integer
description: The user ID.
title_id:
type: integer
description: The title ID.
is_tv:
type: boolean
description: Whether the content is a TV show.
genre:
type: string
description: The genre.
enum: [comedy, action, drama]
average_rating:
type: number
description: The title's average rating.
minimum: 0
maximum: 10
required: [average_rating, genre, is_tv, title_id, user_id]
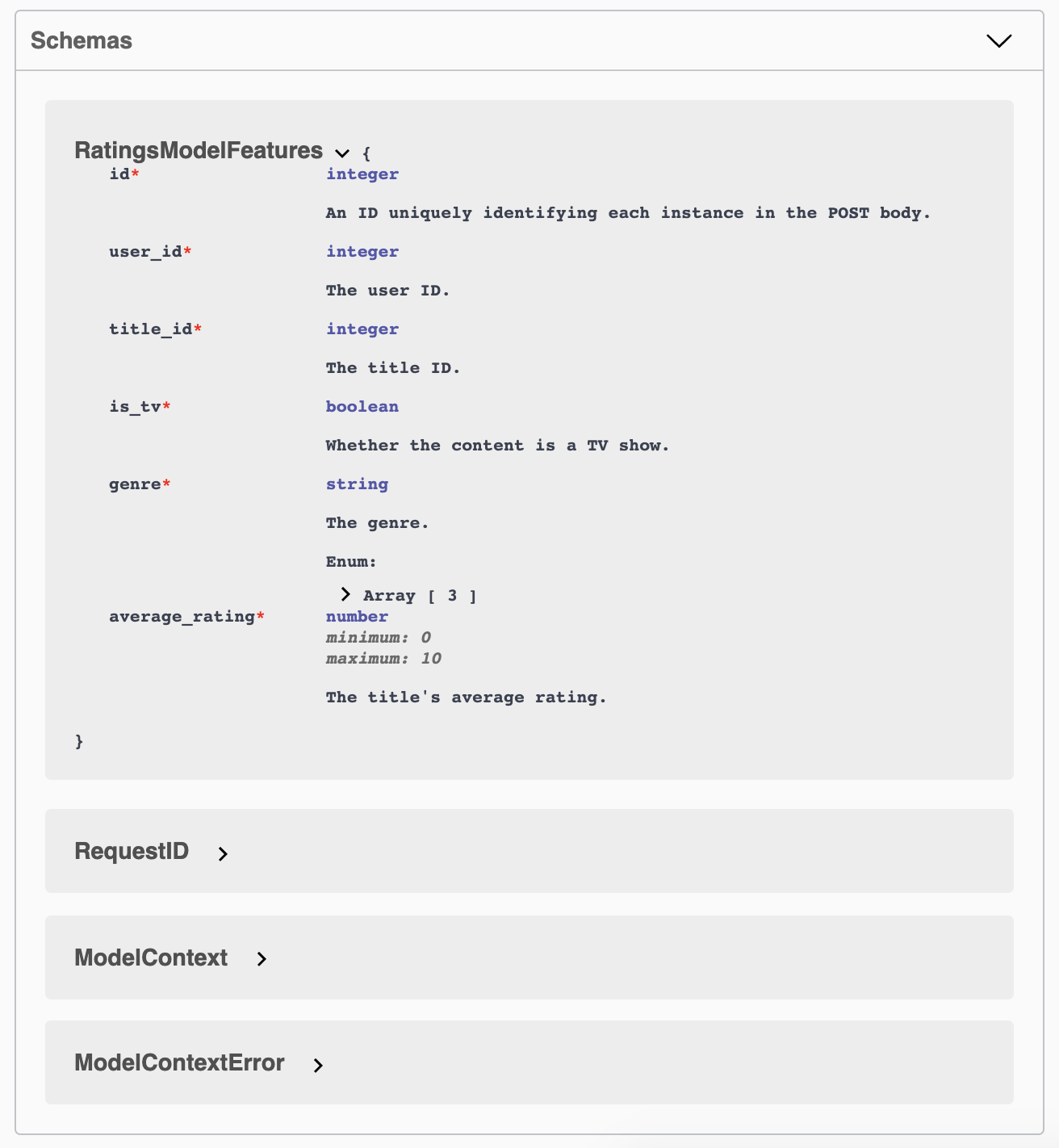
PredictionService adds a required integer field, id, to the schema. Also, by default, PredictionService performs batch prediction over multiple objects, and thus the above would become the item type for an Array. These modifications are roughly equivalent to:
instance_schema = Object(properties={'id': Integer(), **feature_schema.properties})
batch_schema = Array(item_type=instance_schema)
resulting in the following OpenAPI spec which describes an acceptable payload for a PredictionService instantiated with PredictionService(..., feature_schema=feature_schema)
type: array
items:
type: object
properties:
average_rating:
description: The title's average rating.
maximum: 10
minimum: 0
type: number
genre:
description: The genre.
enum:
- comedy
- action
- drama
type: string
id:
description: 'An ID uniquely identifying each instance in the POST body.'
type: integer
is_tv:
description: Whether the content is a TV show.
type: boolean
title_id:
description: The title ID.
type: integer
user_id:
description: The user ID.
type: integer
required:
- average_rating
- genre
- id
- is_tv
- title_id
- user_id
Notice that here item_type is another API object type, in this case Object. Both Array.item_type and Object.properties are composable in this way, and will be implemented using OpenAPI $ref if reference_name is given.
Schema Validation¶
We can add input validation against the above schema to the PredictionService in Getting Started like so:
prediction_service = PredictionService(
model=my_model,
name='my-model',
api_version='v1',
feature_schema=feature_schema,
validate_request_data=True)
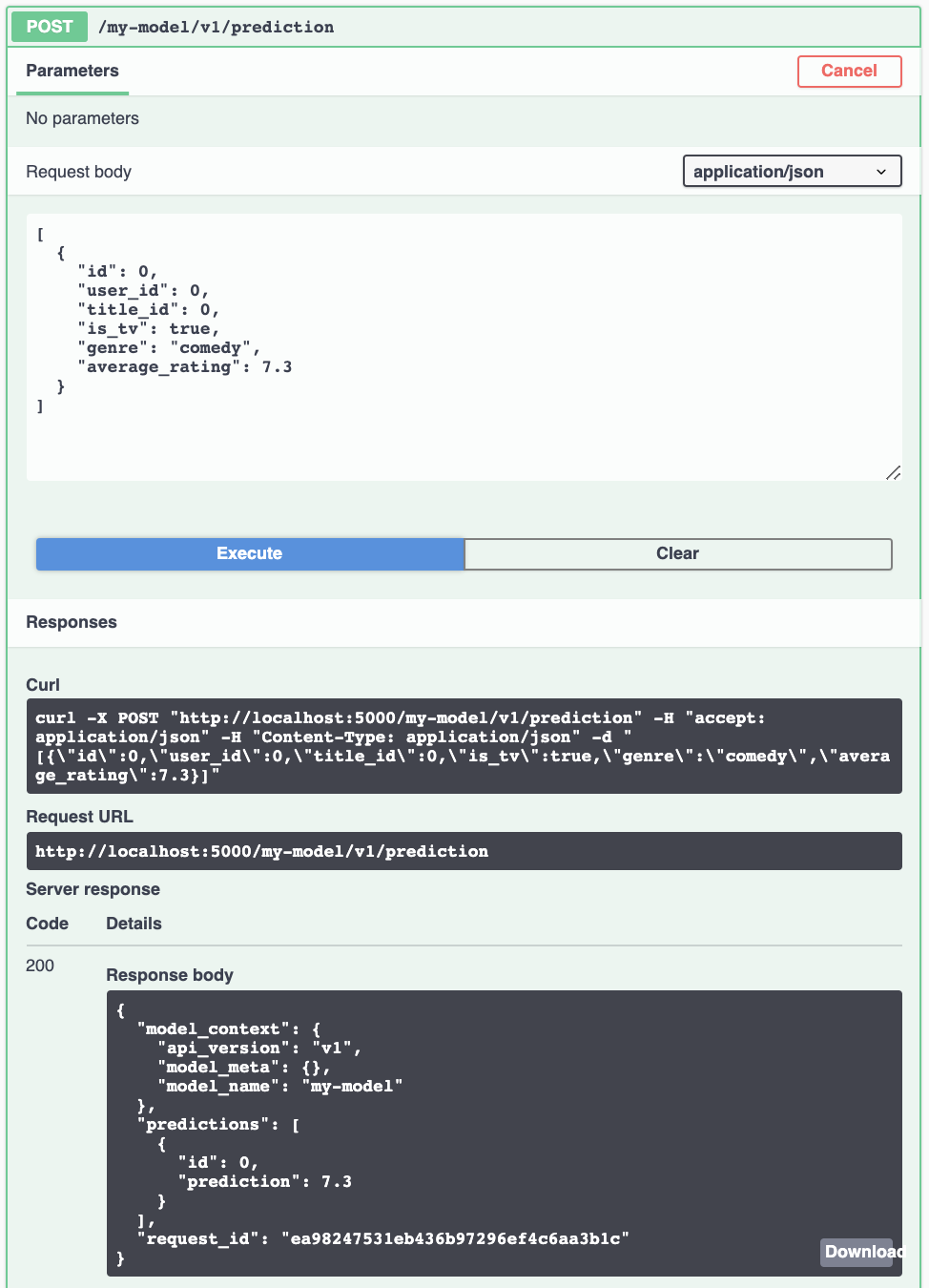
Now, for valid input such as
[
{
"id": 1,
"user_id": 122333,
"title_id": 444455555,
"is_tv": true,
"genre": "comedy",
"average_rating": 6.7
},
{
"id": 2,
"user_id": 122333,
"title_id": 788999,
"is_tv": false,
"genre": "drama",
"average_rating": 4.3
}
]
we receive predictions as expected, but input such as
[
{
"id": 1,
"user_id": 122333,
"title_id": 444455555,
"genre": "not-a-real-genre",
"average_rating": 6.7
},
]
will result in a 422 error (Unprocessable Entity). Error handling is discussed further in this section.
Schema Documentation¶
To expose Swagger documentation automatically, simply add expose_docs=True to the porter.services.ModelApp constructor. porter will also set the name and description attributes, which will appear in the documentation.
app = ModelApp(
[prediction_service],
name='Example Model',
description='Minimal example of a model with input validation and documentation.',
expose_docs=True)
If this app is run in testing mode, docs are now available at http://localhost:5000/docs/. The top of the page shows the name and description of the app, followed by information about the exposed endpoints:
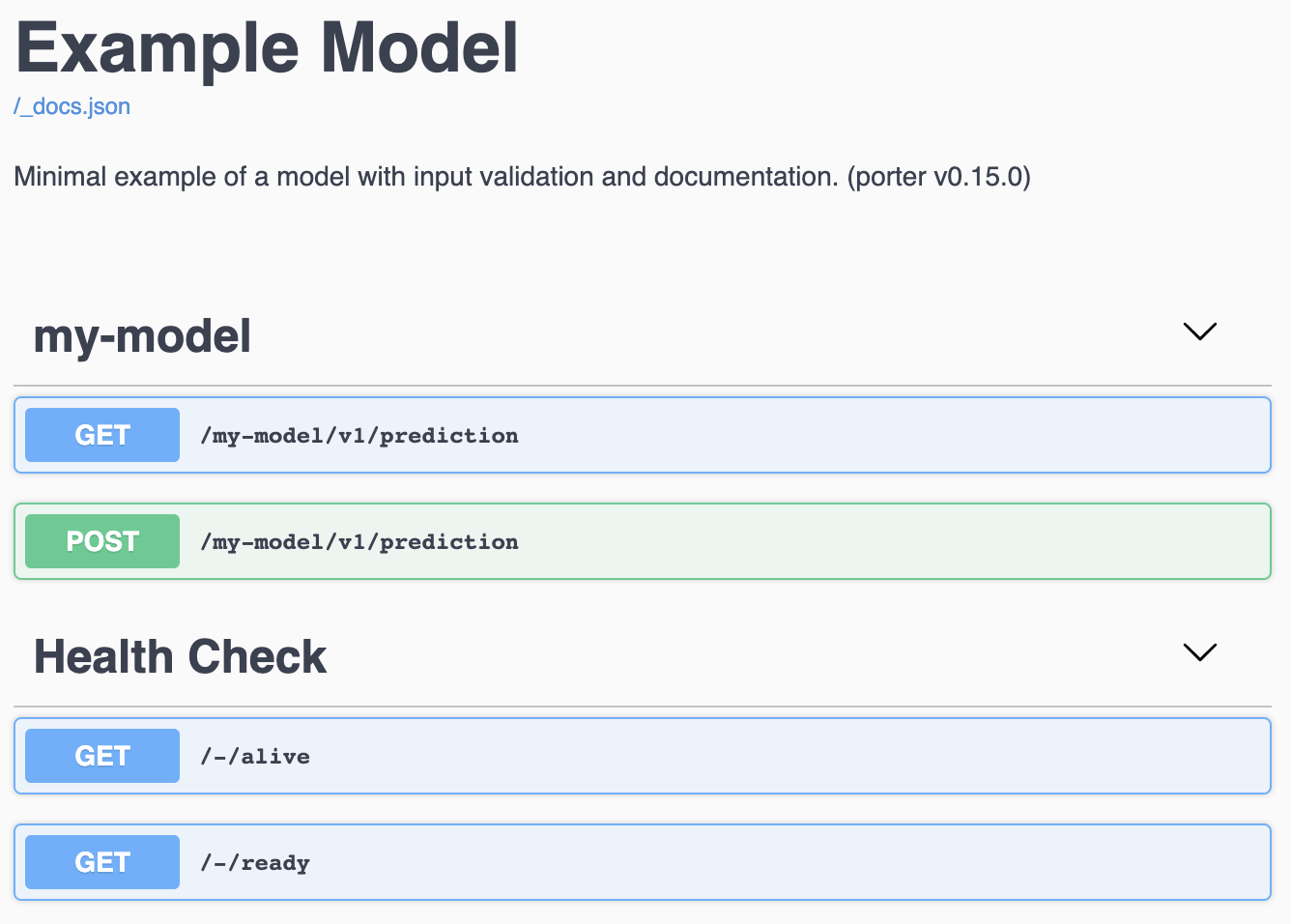
At the bottom of the page, we find a list of schemas which can be unfolded and inspected:
The endpoint documentation can be unfolded, and you can select “Try it out” to test it:
Accessing the OpenAPI Spec¶
The automatically generated OpenAPI spec used to render the Swagger documentation shown above can be
accessed directly from the porter.services.ModelApp instance.
app = ModelApp(..., expose_docs=True)
app.docs_json
This attribute is useful for programmatically inspecting the documentation. Additionally, users may mutate this object (so long as it adheres to the OpenAPI standard), thereby overriding any aspect of the OpenAPI spec served.